Thyroid Diseases
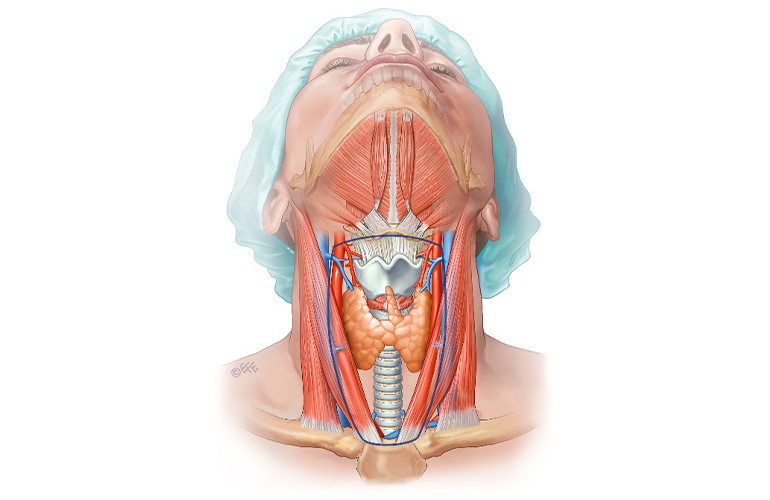
General SurgeryThe thyroid gland is a butterfly-like endocrine gland located in the neck in front of the trachea, under the thyroid cartilage called the Adam's apple. Under normal conditions, it weighs 20-25 grams. It secretes the hormones it produces into the blood, therefore it has a rich blood and lymph vascular network. Mainly thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and calcitonin hormone are produced in the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland secreting too much hormone is called "Hyperthyroidism" and producing too little hormone is called "Hypothyroidism". The condition of excess thyroid hormone in the blood is called thyrotoxicosis, commonly known as toxic goiter.
What is goiter?
Any non-tumoral growth of the thyroid gland is called goiter. It can be caused by many reasons. Having goiter in an individual does not always mean that the gland is overactive. A similar situation may occur in underactive glands. Treatment methods may include various drug treatments or surgery, depending on the underlying cause.
Hyperthyroidism
Excessive hormone secretion by the thyroid gland may occur for various reasons. The gland may be nodular or diffusely altered. In case of hyperthyroidism, the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are detected to be high in the blood, while the level of TSH, whose main function is to stimulate the secretion of hormones from the thyroid and secreted from the pituitary gland, is detected to be low.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism; Weakness, palpitations, irritability, intolerance to heat, weight loss despite increased appetite, sweating, diarrhea, shortness of breath, and decreased menstrual bleeding may occur. In some specific diseases, a bright look and protrusion of the eyes may be observed.
Causes of hyperthyroidism:
• Toxic multinodular goiter
• Toxic adenoma
• Basedow Graves disease
• Certain periods of some thyroiditis
• Pregnancy hyperthyroidism
• Hyperthyroidism due to excessive iodine or thyroid hormone intake
Hyperthyroidism treatment
The aim of treatment is to eliminate the symptoms caused by thyroid hormones, which directly affect the metabolic rate. Generally, initial treatment is the use of antithyroid drugs that work by stopping the synthesis of thyroid hormones. For this purpose, methimazole or propylthiouracil is used, especially in pregnant women. If hyperthyroidism does not improve after 6 months to 1 year of treatment after starting drug treatment, either radioactive iodine, popularly known as atomic therapy, or surgical treatment can be applied.
Causes of hypothyroidism
It is a common hormonal disorder, although its clinical findings do not always appear fully. Its frequency increases especially in women and with increasing age. In case of hypothyroidism, the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are detected to be low in the blood, while the TSH level is detected to be high as the need increases.
Findings generally increase in parallel with the decrease in hormones. In subclinical conditions, only the hormone profile is impaired and may not cause obvious symptoms. Fatigue, weakness, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, dry hair, joint pain, chills, constipation, menstrual irregularity, depression, infertility, blunted perception, in advanced cases, hoarse voice, hard edema under the skin may occur.
The most common cause of hypothyroidism in society, especially among women; Hashimoto's thyroiditis, which can be defined as a type of inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland, is the removal of the thyroid gland with thyroid surgery and radioactive iodine treatment. In its treatment, it can be supported with thyroid medications.