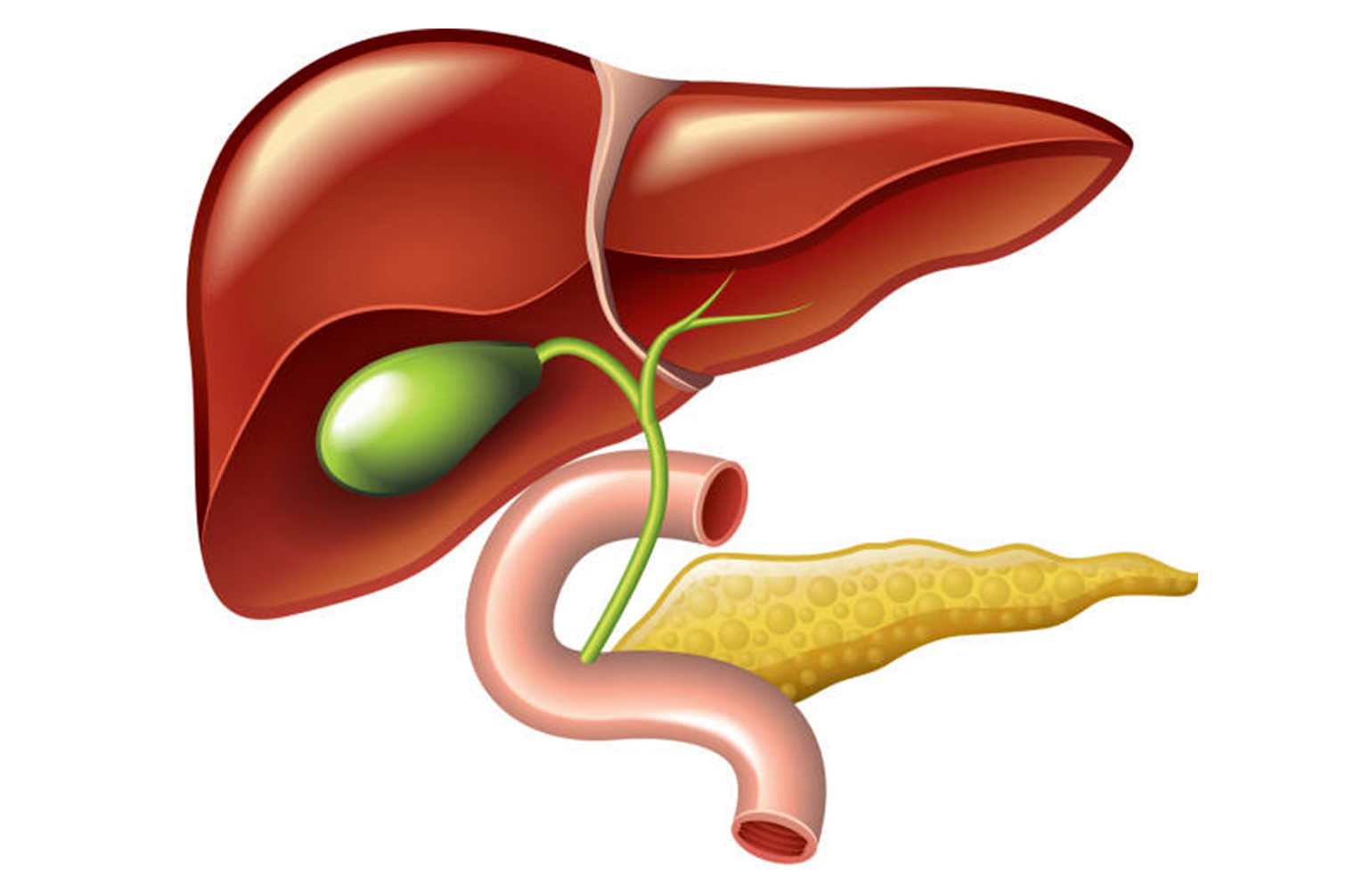
Gallbladder Cancer
Oncological SurgeryGallbladder cancer is a rare, rapidly progressing digestive system cancer with a poor survival rate. It has a high incidence and mortality rate in India, Chile and Japan in the world. It is an insidious disease and is usually found incidentally in tissue samples from surgeries where the gallbladder is removed (cholecystectomy) due to gallstones.
Causes of Gallbladder Cancer
The causes that lead to gallbladder cancer are not fully known. Most gallbladder cancers begin in the cells that line and secrete the inside of the gallbladder. It is hypothesized that these cells lose their similarity to each other due to chronic irritation due to long-standing gallstones and turn into invasive carcinoma. It is accepted that this change takes 5-10 years.
The prevalence of gallbladder cancer in the population is highly similar to gallstones. Cancer can be seen in 0.5-3% of gallbladder stones.
Grape-like growths of wall tissue inside the gallbladder, such as gallbladder polyps, also increase the risk of cancer. Especially in patients over the age of 50, the possibility of cancer on the basis of gallbladder polyps increases when the gallbladder polyp is larger than 1 cm, there are more than one, or if it grows during follow-up.
The incidence of cancer in cases of porcelain bladder (where the gallbladder wall is completely calcified), which is the most advanced form of chronic inflammation, is 25%. Therefore, cholecystectomy is indicated in all porcelain bladders.
Apart from this, some parasites that are not common in our country may also form the basis.
Additionally, receiving methyldopa, oral contraceptives, isoniazid therapy and working in the tire industry are considered predisposing factors.
Gallbladder Cancer Treatment
The main treatment for gallbladder cancer is surgery. The extent of surgical treatment of gallbladder cancer is determined by the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor, and whether the surgery is primary or not.
In some cases, it may be necessary to remove tissue from the lobes of the liver along with the gallbladder, or resection of the bile ducts within the liver and removal of the surrounding lymphatic tissue.